
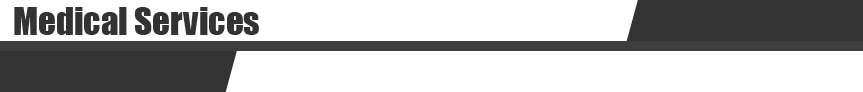


General examination – Every pet receives a detailed evaluation of the visual system function, and examination of the front and back part of the eye, eyelids and orbit during each eye examination.
Eyelids and the front part of the eye (cornea, anterior chamber, lens) are evaluated with a very specialized microscope (slit lamp biomicroscope), while the back part of the eye (vitreous, retina, optic nerve) is evaluated with the special optical instrument called indirect ophthalmoscope.
»back to top
Tonometry – Tonometry is a diagnostic procedure for the evaluation of intraocular pressure. We use special electronic instrument equipped with the pressure sensor, which very precisely evaluates intraocular pressure in many species: dogs, cats, rabbits, birds, hamsters, pet mice and rats. Elevated intraocular pressure can cause rapid damage to the back part of eye and result in the complete blindness within 12 hours. Early detection of the elevated intraocular pressure is an essential step for prevention of blindness in many pets. Tonometry is performed with the application of numbing drops (topical anesthetic), so eye discomfort is minimally present during this examination procedure.
»back to top
Tear production testing – We routinely perform tear production testing to evaluate your pet eyes for a possible presence of the “dry eye disease”. Dry eye disease is a frequent cause of ocular discomfort, irritation and may ultimately result in the serious injury to the eye and blindness.
»back to top
Special stains (fluorescein stain, rose Bengal stain, lysamine green stain) – Special staining procedures are used to detect corneal ulcers and different eye abnormalities, which can result in the damage to the front part of the eye and decreased vision.
»back to top
Nasolacrimal duct evaluation – Nasolacrimal duct is a tube, which drains tears from the eye to the nose or mouth. Sometimes this duct can be clogged or damaged, which may result in the excessive tearing or discharge from the eye. We use a special probe to inspect whether duct allows normal flow of the tears.
»back to top
Chromatic pupil light reflex (cPLR) testing – cPLR testing is a special diagnostic procedure, which was initially developed by Dr Grozdanic and his research team at the Iowa State University in 2006. Since that time this technology became a popular veterinary ophthalmology tool for the evaluation of the eye function in six different continents. This particular technique allows for the early detection of the retina and optic nerve abnormalities, even before any vision problems occur.
»back to top
Electroretinography (ERG) – Electroretinography is a special diagnostic routine in which an ophthalmologist is recording electrical activity coming from the back part of the eye in your pet. This particular technique is particularly useful for an early detection of photoreceptor/retina diseases. Photoreceptors are cells, which are converting the light signal in the electrical signal information, which is than transmitted from the eye to the brain. The ERG evaluation is performed with the use of topical numbing drops after patients have been dark adapted for 20 minutes. In pets which have the high level of anxiety, a mild sedation may have to be used to complete this examination.
»back to top
Ocular ultrasound – The ultrasound examination of the eye and orbit is pursued in pets where direct observation of intraocular structures is not possible, or there is a suspicion that the problem may be located behind the eye (in the orbit). We also perform a special form of ultrasonography – high frequency ultrasonography with a goal of detecting early abnormalities in the front part of the eye, which can result in the abnormal flow of the eye fluid (aqueous humor) from the eye. The abnormalities in the eye fluid outflow may result in the increased intraocular pressure, which may cause blindness in the less than 12 hours. The ocular ultrasound evaluation is performed with the use of topical numbing drops after patients, however in pets which have the high level of anxiety, a mild sedation may have to be used to complete this examination.
»back to top


